Hampshire
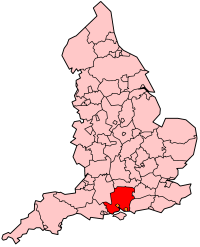
Hampshire's Location within England |

Hampshire's Coat of Arms |
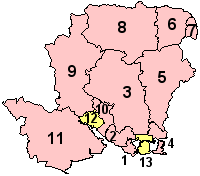
- Gosport
- Fareham
- Winchester
- Havant
- East Hampshire
- Hart
- Rushmoor
- Basingstoke
and Deane
- Test Valley
- Eastleigh
- New Forest
- Southampton
(Unitary)
- Portsmouth
(Unitary)
|
Hampshire
(abbr. Hants) is a county on the south coast of England
in the United Kingdom. The county borders (clockwise from West), Dorset,
Wiltshire, Berkshire,
Surrey and West Sussex.
The county is 1,455 square miles (3,769 km²) in size and at its widest
points is approximately 55 miles (90 km) east-west and 40 miles (65 km)
north-south. The county town is Winchester
situated at 51°03'35?N, 1°18'36?W. The 2001 census gave the population
of the administrative county as 1.24 million; the ceremonial county also
includes the cities of Portsmouth
and Southampton, which are administratively
independent, and has a total population of 1.6 million.
Hampshire
is a popular holiday area, with tourist attractions including its many
seaside resorts, the maritime area in Portsmouth,
and the motor museum at Beaulieu.
The New Forest National Park lies within the borders, as does a large
area of the South Downs, which is also scheduled to become a National
Park. Hampshire has a long maritime history and
two of England's largest ports lie on its coast. The county is famed as
home of the writers Jane Austen and Charles Dickens.
| Geography |
| Status |
Ceremonial &
(smaller) Non-metropolitan county |
| Region |
South East England
|
Area
- Total
- Admin Council
- Admin Area |
Ranked 9th
3,769 km²
Ranked 8th
3,679 km² |
| Admin HQ |
Winchester
|
| ISO 3166-2 |
GB-HAM |
| ONS code |
24 |
| NUTS 3 |
UKJ33 |
| Demographics |
Population
- Total (2002 est.)
- Density
- Admin Council
- Admin Pop.
|
Ranked 5th
1,663,000
441 / km²
Ranked 3rd
1,253,300 |
| Ethnicity |
96.7% White
1.3% S. Asian |
| Politics
|
| Executive |
Conservative |
| Members of Parliament |
James Arbuthnot
John Denham
Sandra Gidley
Mike Hancock
Mark Hoban
Gerald Howarth
Chris Huhne
Julian Lewis
Michael Mates
Sarah McCarthy-Fry
Maria Miller
Mark Oaten
Desmond Swayne
Peter Viggers
Alan Whitehead
David Willetts
George Young |
Physical geography
Hampshire's geology
falls into two categories. In the south, along the coast is the "Hampshire
Basin", an area of relatively non-resistant Eocene and Oligocene
clays and gravels which are protected from sea erosion by the Isle of
Purbeck, Dorset, and the Isle of Wight. These
low, flat lands support heathland and woodland habitats, a large area
of which form part of the New Forest. The New Forest has a mosaic of heathland,
grassland, coniferous and deciduous woodland habitats that host diverse
wildlife. The forest is protected as a national park, limiting development
and agricultural use to protect the landscape and wildlife. Large areas
of the New Forest are open common lands kept as a grassland plagioclimax
by grazing animals, including domesticated cattle, pigs and horses, and
several wild deer species. Erosion of the weak rock and sea level change
flooding the low land has carved several large estuaries and rias, notably
the 12 mile (19 km) long Southampton Water and the large convoluted Portsmouth
Harbour. The Isle of Wight lies off the coast
of Hampshire where the non-resistant rock has
been eroded away forming the Solent.
In the north and centre
of the county the substrate is the Southern England Chalk Formation of
Salisbury Plain and the South Downs. These are high hills with steep slopes
where they border the clays to the south. The hills dip steeply forming
a scarp onto the Thames valley to the north, and dip gently to the south.
The highest point in the county is Pilot Hill, which reaches the height
of 286 m (938 ft). The downland supports a calcareous grassland habitat,
important for wild flowers and insects. In the past Hampshire
had little arable agriculture, but in the early 20th century the demand
for food led to the establishment of farms on the downs. A large area
of the downs are now protected from further agricultural damage by the
East Hampshire Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty The Itchen and Test
are trout rivers that flow from the chalk through wooded valleys into
Southampton Water.
Hampshire has a milder
climate than most areas of the British Isles, being in the far south with
the climate stabilising effect of the sea, but protected against the more
extreme weather of the Atlantic coast. Hampshire
has a higher average annual temperature than the UK average at 10.2 °C
to 12 °C, average rainfall at 741–1060 mm per year, and higher
than average sunshine at over 1541 hours per year.
History
The chalk downland
of the South Downs and southern edges of Salisbury Plain were settled
in the neolithic, and these settlers built hill forts and may have farmed
the valleys of Hampshire. Hampshire
was part of an area named Gwent or Y Went by the Celts, which also covered
areas of Somerset and Wiltshire.
In the Roman invasion of Britain, Hampshire was
one of the first areas to fall to the invading forces. The county was
occupied by Jutish tribes until Saxon times. Hampshire was one of the
first Saxon shires, recorded in 755, but for two centuries represented
the western end of Saxon England, as advances into Dorset
and Somerset were fought off by the Britons. After
the Saxons advanced west Hampshire became the
centre of the Kingdom of Wessex, and many Saxon kings are buried at Winchester.
A statue in Winchester celebrates
the powerful King Alfred, who stabilised the region in the 9th century.
 After
the Norman Conquest the county was favoured by Norman kings who established
the New Forest as a hunting forest. The county was recorded in the Domesday
Book divided into 44 hundreds. From the 12th century the ports grew in
importance, fuelled by trade with the continent, wool and cloth manufacture
in the county, and the fishing industry, and a shipbuilding industry was
established. After
the Norman Conquest the county was favoured by Norman kings who established
the New Forest as a hunting forest. The county was recorded in the Domesday
Book divided into 44 hundreds. From the 12th century the ports grew in
importance, fuelled by trade with the continent, wool and cloth manufacture
in the county, and the fishing industry, and a shipbuilding industry was
established.
Over several centuries
a series of castles and forts were constructed along the coast of the
Solent to defend the harbours at Southampton
and Portsmouth. These include
the Norman Portchester Castle which overlooks Portsmouth Harbour, and
a serious of forts built by Henry VIII including Hurst Castle, situated
on a sand spit at the mouth of the Solent, Calshot Castle on another spit
at the mouth of Southampton Water, and Netley Castle. Southampton
and Portsmouth remained important
harbours when rivals, such as Poole and
Bristol declined, as they are amongst
the few locations that combine shelter with deep water. Southampton
has been host to many famous ships, including the Mayflower and the Titanic,
the latter being staffed largely by Hampshire natives.
 Hampshire
played a large role in World War II due to its large Royal Navy harbour
at Portsmouth, the army camp
at Aldershot and the military
Netley Hospital on Southampton Water, as well as its proximity to the
army training ranges on Salisbury Plain and Purbeck. Supermarine, the
designers of the Spitfire and other military aircraft, were based in Southampton,
which led to severe bombing of the city. Aldershot
remains one of the British Army's main permanent camps. Hampshire
played a large role in World War II due to its large Royal Navy harbour
at Portsmouth, the army camp
at Aldershot and the military
Netley Hospital on Southampton Water, as well as its proximity to the
army training ranges on Salisbury Plain and Purbeck. Supermarine, the
designers of the Spitfire and other military aircraft, were based in Southampton,
which led to severe bombing of the city. Aldershot
remains one of the British Army's main permanent camps.
The county has in the past been called "Southamptonshire" and
appears as such on some Victorian maps. Its name was officially changed
from 'County of Southampton' to 'County of Hampshire' on April 1, 1959.
The short form of the name, often used in postal addresses, is Hants.
The Isle
of Wight and the Channel Islands have traditionally been treated as
part of Hampshire for some purposes, but have
been administratively independent for over a century, with the Isle
of Wight obtaining a county council of its own in 1890. The Isle
of Wight became a full ceremonial county in 1974. Apart from a shared
police force there are now no formal administrative links between the
Isle of Wight and Hampshire,
though many organisations still combine Hampshire,
Isle of Wight and the Channel Islands. The
towns of Bournemouth and Christchurch
also fall within the traditional county of Hampshire,
but were ceded to Dorset in the local government
reorganisation of 1974.
Economy
Hampshire is a relatively
affluent county, with a Gross domestic product (GDP) of £22.9 billion
(£16.3 billion when excluding Southampton
and Portsmouth). This makes it
the sixth largest economy in England,
and is equal in size to the economy of Northern Ireland, making up 2%
each of the economy of the UK as a whole. In terms of GDP per head Hampshire
is just above the national average at 105% (37th highest in England),
rising to 122% when including Southampton
and Portsmouth. The highest GDP
per head is Portsmouth at 144%
of the national average.
 Portsmouth
and Winchester have the highest
job densities in the county, and there is therefore a high level of commuting
into the cities. Southampton
has the highest number of total jobs and commuting both into and out of
the city is high. The county has a lower level of unemployment than the
national average, at 1.9% when the national rate was 3.3%, and as of March
2005 has fallen to 1.1%. 39% are employed by large firms, compared to
a national average of 42%. Hampshire has a considerably
higher than national average employment in high-tech industries, but average
levels in knowledge based industry. 25.21% of the population work in the
public sector. Portsmouth
and Winchester have the highest
job densities in the county, and there is therefore a high level of commuting
into the cities. Southampton
has the highest number of total jobs and commuting both into and out of
the city is high. The county has a lower level of unemployment than the
national average, at 1.9% when the national rate was 3.3%, and as of March
2005 has fallen to 1.1%. 39% are employed by large firms, compared to
a national average of 42%. Hampshire has a considerably
higher than national average employment in high-tech industries, but average
levels in knowledge based industry. 25.21% of the population work in the
public sector.
Many rural areas of
Hampshire have traditionally been reliant on
agriculture, though the county was less agricultural than most surrounding
counties, and was mostly concentrated on dairy farming. The significance
of agriculture as an employer and wealth creator has declined since the
first half of the 20th century and agriculture currently employs 1.32%
of the population. The New Forest area is a National Park, and tourism
is a significant economic segment in this area.
The cities of Southampton
and Portsmouth are both significant
ports, with Southampton handling
a large proportion of the national container freight and Portsmouth
housing a large Royal Navy base. The docks have traditionally been large
employers in these cities, though again mechanisation has forced diversification
of the economy.
Demographics
 At
the Census 2001 [6] the ceremonial county recorded a population of 1,644,249,
of which 1,240,103 were in the administrative county, 217,445 were in
the unitary authority of Southampton,
and 186,701 were in Portsmouth.
The population of the administrative county grew 5.6% from the 1991 census,
Southampton grew 6.2% while
Portsmouth remained unchanged,
compared with 2.6% for England
and Wales as a whole. Eastleigh
and Winchester grew fastest at
9% each. The age structure of the population is similar to the national
average. At
the Census 2001 [6] the ceremonial county recorded a population of 1,644,249,
of which 1,240,103 were in the administrative county, 217,445 were in
the unitary authority of Southampton,
and 186,701 were in Portsmouth.
The population of the administrative county grew 5.6% from the 1991 census,
Southampton grew 6.2% while
Portsmouth remained unchanged,
compared with 2.6% for England
and Wales as a whole. Eastleigh
and Winchester grew fastest at
9% each. The age structure of the population is similar to the national
average.
96.73% of residents
were indigenous, falling to 92.37% in Southampton.
The significant ethnic minorities are Asian at 1.34% and mixed race at
0.84%. 0.75% of residents were migrants from outside the UK. 73.86% stated
their religion as Christianity and 16.86% were not religious. Significant
minority religions were Islam (0.76%) and Hinduism (0.33%).
Politics
Hampshire
is divided into seventeen parliamentary constituencies. Ten of these are
represented by Conservative MPs, four by the Liberal Democrats and three
by Labour. Labour represent the large cities, including both Southampton
constituencies (Test and Itchen) and Portsmouth North. The Conservatives
represent the most rural constituencies, Aldershot,
New Forest West, New Forest East, Hampshire North West, Basingstoke,
Hampshire North East, Hampshire East, Havant,
Gosport and Fareham.
The Liberal Democrats represent Winchester,
Romsey, Portsmouth South and Eastleigh,
all centred around towns.
At the 2005 local
elections for Hampshire County Council the Conservative Party had a 43.69%
share of the votes, the Liberal Democrats had 36.01% and Labour 16.08%.
Therefore 46 Conservatives, 28 Liberal Democrats and four Labour councillors
sit on the County Council. Southampton City Council, which is entirely
independent, has 18 Liberal Democrat, 15 Labour and 15 Conservative councillors.
Portsmouth City Council, also independent, has 20 Liberal Democrat, 18
Conservative, seven Labour and one independent councillor.
Cities, Towns and Villages
 Hampshire's
county town is Winchester, a
historic city that was once the capital of the ancient kingdom of Wessex.
The port cities of Southampton
and Portsmouth were split off
as independent unitary authorities in 1997, although they are still included
in Hampshire for ceremonial purposes. Fareham,
Gosport and Havant
have grown into a conurbation that stretches along the coast between the
two main cities. The three cities are all university cities, Southampton
being home to the University of Southampton and Southampton Solent University
(formerly Southampton Institute), Portsmouth
to the University of Portsmouth, and Winchester
to the University of Winchester (formerly known as University College
Winchester; King Alfred's College). Hampshire's
county town is Winchester, a
historic city that was once the capital of the ancient kingdom of Wessex.
The port cities of Southampton
and Portsmouth were split off
as independent unitary authorities in 1997, although they are still included
in Hampshire for ceremonial purposes. Fareham,
Gosport and Havant
have grown into a conurbation that stretches along the coast between the
two main cities. The three cities are all university cities, Southampton
being home to the University of Southampton and Southampton Solent University
(formerly Southampton Institute), Portsmouth
to the University of Portsmouth, and Winchester
to the University of Winchester (formerly known as University College
Winchester; King Alfred's College).
Hampshire
lies outside the green belt area of restricted development around London,
but has good railway and motorway links to the capital, and in common
with the rest of the south-east has seen the growth of dormitory towns
since the 1960s. Basingstoke,
in the north of the county, has grown from a country town into a business
and finance centre. Aldershot,
Portsmouth, and Farnborough
have strong military associations with the Army, Royal Navy and Royal
Air Force respectively. The county also includes several market towns;
Andover, Bishop's
Waltham, Lymington, Petersfield,
Ringwood, Romsey,
and Whitchurch.
Towns by population size: (2004
est.)
Southampton
- 221,100
Portsmouth - 188,700
Havant - 116,300
Fareham - 107,977
Winchester - 35,200
Culture, Arts and Sport
 Hampshire
has literary connections, being the birthplace of authors including Jane
Austen, Charles Dickens and Charles Kingsley. Austen lived most of her
life in Hampshire, where her father was rector
of Steventon, and wrote all of her novels in the county. Hampshire
also has many visual art connections, claiming the painter John Everett
Millais as a native, and the cities and countryside have been the subject
of paintings by L. S. Lowry and J. M. W. Turner. Hampshire
has literary connections, being the birthplace of authors including Jane
Austen, Charles Dickens and Charles Kingsley. Austen lived most of her
life in Hampshire, where her father was rector
of Steventon, and wrote all of her novels in the county. Hampshire
also has many visual art connections, claiming the painter John Everett
Millais as a native, and the cities and countryside have been the subject
of paintings by L. S. Lowry and J. M. W. Turner.
Hampshire's relatively
safe waters have allowed the county to develop as one of the busiest sailing
areas in the country, with many yacht clubs and several manufacturers
on the Solent. The sport cricket was largely developed in south-east England,
with one of the first teams forming at Hambledon
in 1750. Hampshire County Cricket Club today is a successful first-class
team, captained by Shane Warne. Hampshire has
several association football teams, the most successful being Premier
League Portsmouth F.C. and Championship side Southampton F.C., which have
traditionally been fierce rivals.
Transport
There is an international
airport with its own rail station situated between Southampton
and Eastleigh, Southampton Airport,
and cross-channel ferries link the city to the Isle
of Wight and European continent. The South Western Main Line railway
from London to Weymouth
runs through Winchester and Southampton,
and the Wessex Main Line from Bristol
to Portsmouth also runs through
the county. The M3 motorway connects the county to London.
The construction of the Twyford Down cutting near Winchester
caused major controversy by cutting through a series of ancient trackways
(the Dongas) and other features of archeeological significance. The M27
motorway serves a bypass for the major conurbations and as a link to other
settlements on the south coast. Other important roads include the A3,
A31 and A36.
The county has a high
level of car ownership, with 15.7% having no access to a private car compared
to 26.8% for England and
Wales. The county has a lower than average use of trains (3.2% compared
to 4.1% for commuting) and buses (3.2% to 7.4%) but a higher than average
use of bicycles (3.5% to 2.7%) and cars (63.5% to 55.3%).
|






 After
the Norman Conquest the county was favoured by Norman kings who established
the New Forest as a hunting forest. The county was recorded in the Domesday
Book divided into 44 hundreds. From the 12th century the ports grew in
importance, fuelled by trade with the continent, wool and cloth manufacture
in the county, and the fishing industry, and a shipbuilding industry was
established.
After
the Norman Conquest the county was favoured by Norman kings who established
the New Forest as a hunting forest. The county was recorded in the Domesday
Book divided into 44 hundreds. From the 12th century the ports grew in
importance, fuelled by trade with the continent, wool and cloth manufacture
in the county, and the fishing industry, and a shipbuilding industry was
established.
 Portsmouth
Portsmouth At
the Census 2001 [6] the ceremonial county recorded a population of 1,644,249,
of which 1,240,103 were in the administrative county, 217,445 were in
the unitary authority of
At
the Census 2001 [6] the ceremonial county recorded a population of 1,644,249,
of which 1,240,103 were in the administrative county, 217,445 were in
the unitary authority of  Hampshire's
county town is
Hampshire's
county town is  Hampshire
Hampshire